PLC Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide for Modern Manufacturing
In today's modern manufacturing, PLC controllers play a crucial role. They are used to control and manage the operations of factories and production lines. PLC controllers are programmed to perform complex functions, such as controlling machines, monitoring processes, and adjusting settings based on real-time data.One of the key benefits of using PLC controllers is their ability to automate processes and reduce human error. This can lead to better accuracy and efficiency in production, as well as increased productivity.Another advantage of PLC controllers is their flexibility and adaptability. They can be easily modified and updated to meet changing demands and technological advancements.Overall, PLC controllers are an essential tool for modern manufacturing. They allow businesses to improve their operations, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
In today's highly automated and digitally driven world, the use of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) has become an indispensable part of modern manufacturing. As a seasoned foreign trade operator, understanding the principles behind these controllers is crucial to effectively managing and expanding your business. Let's delve into this topic and explore how PLCs can revolutionize your production lines while maintaining a focus on practical application scenarios.
At its core, a PLC is a device that executes instructions written in a special type of programming language known as Programmable Logic Statement Language (PLC-SLC). These controllers are designed specifically to handle complex control tasks within industrial environments, offering high reliability and flexibility. In essence, their primary function is to manage, monitor, and automate various processes by controlling physical devices like motors, sensors, and actuators.
To begin with, let's talk about what makes PLCs so versatile. First, they come in various forms, each tailored to different applications. For instance, there are microcontroller-based controllers, which are small enough to be placed directly on the machine tool or within the workpiece, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs), which are larger and more capable of handling larger systems. Regardless of their size or design, all PLCs share a similar structure, consisting of input modules, output modules, and central processing unit (CPU), all connected via a network of communication lines.
Now, let's dive deeper into the functionality of a typical PLC. At its simplest level, a PLC can be thought of as a microcomputer with built-in software capable of executing instructions. This software is typically programmed in a high-level language like ladder diagrams, function blocks, or SLC. When an instruction from the software is received by the CPU, it is executed based on the data inputs and the predefined logic rules. This process continues until a desired result, such as turning off a motor or adjusting a temperature, is achieved.
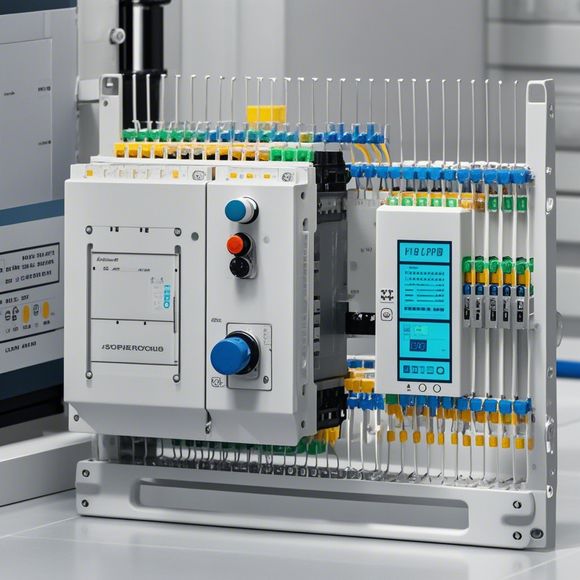

The beauty of PLCs lies in the fact that they allow for a high degree of automation without sacrificing flexibility. By using PLCs, manufacturers can create complex control systems with minimal human intervention, making them ideal for high-volume, low-complexity tasks. Additionally, PLCs offer robust safety features such as overheating protection, short circuit protection, and fault detection, ensuring optimal performance even in adverse conditions.
One common application of PLCs is in assembly lines where robots and other machinery are controlled by these controllers. By programming specific sequences of movements and operations, PLCs ensure that each stage in the process runs smoothly and efficiently. For example, a PLC can be programmed to start a machine tool when a certain part is detected, followed by a sequence of cutting and finishing operations before the finished product is packaged and dispatched.
Another area where PLCs shine is in process automation. Here, the controller is responsible for monitoring various variables such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates. Using advanced algorithms and real-time data analytics, the PLC can make informed decisions about when to intervene, adjust settings, or even shut down the system if necessary. For instance, a PLC might detect an increase in temperature during a chemical reaction and automatically shut down the process to prevent any undesirable outcomes.
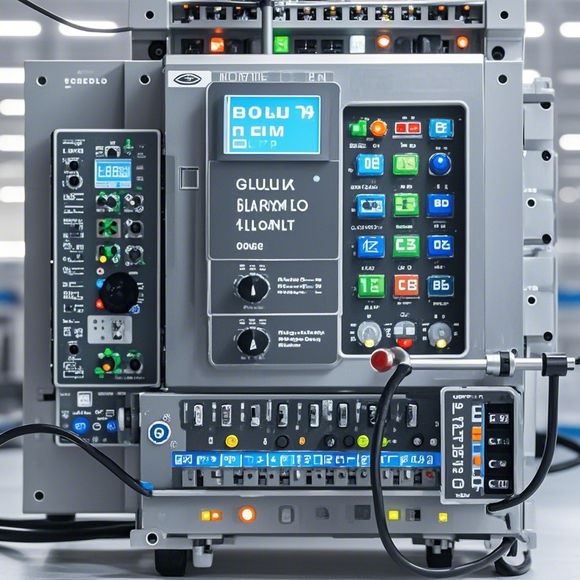

When it comes to integrating PLCs into your foreign trade operation, there are several key factors to consider. Firstly, you need to choose the right PLC model that fits your specific needs and budget. This includes factors like memory capacity, processing speed, and connectivity options. Once you've made this decision, the next step is to develop a detailed plan for programming and testing the PLC system. This may involve working with a specialized firm or hiring an experienced technician who understands both the hardware and software aspects of PLC control.
Additionally, it's essential to consider the regulatory requirements of your target market. While many countries do not have strict regulations on PLCs, some industries may have specific standards or certifications that must be met. Therefore, conducting thorough research and consulting with experts in your industry or country is critical to ensuring compliance.
Finally, once your PLC system is up and running, ongoing maintenance and upgrades are necessary to keep it performing at peak efficiency. This includes regular checks for software updates, hardware replacements when necessary, and troubleshooting any issues that arise. With careful management and attention to detail, PLCs can be powerful tools in driving productivity and improving quality control within your foreign trade operations.
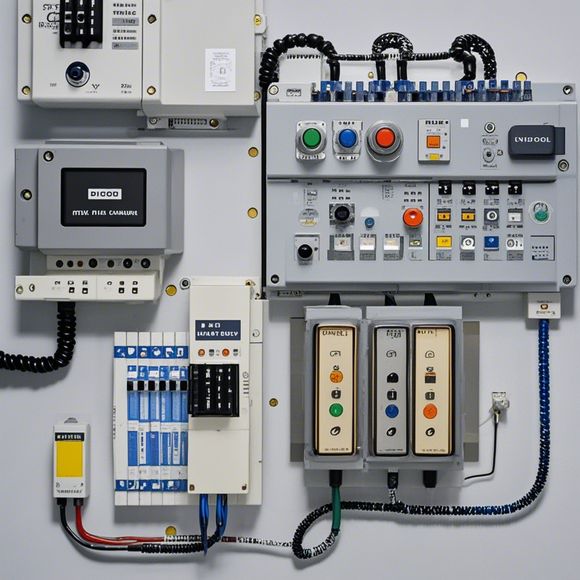
As an experienced foreign trade operator, it's important to recognize the significance of PLCs in modern manufacturing. From their versatile nature to their ability to automate complex control tasks, these controllers represent a significant advancement in the field. By understanding their principles and applying them effectively, you can optimize your supply chain, reduce waste, and enhance overall efficiency. Remember, investing in PLC technology can lead to long-term benefits for your business and help you stay ahead of the competition.
Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Mastering the Art of Plc Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understand and Implement
PLC Controller Wiring Guideline
PLC Programming for Automation Control in the Manufacturing Industry
How to Use a PLC Controller for Your Business