PID Controller Design for Automated Manipulation Systems
PID controller design is crucial for automated manipulation systems. It's an algorithm that adjusts the system's parameters to maintain a steady state. The P stands for Proportional, which ensures that the system reacts quickly to changes in its environment. The I stands for Integral, which adds the effect of the previous state on the current response. Finally, the D stands for Differential, which takes into account the rate of change of the output and the desired change.When designing the PID controller for an automation system, it's important to understand the system's dynamics and how it responds to changes. This involves setting appropriate gain values for each component of the PID algorithm. For example, if the system is sensitive to changes in temperature, then the proportional term will need to be set high to compensate for the rapid changes in temperature. Similarly, if the system is slow to respond to changes, then the integral term can be used to smooth out any noise or disturbances. Finally, the differential term can be used to ensure that the system always moves towards its desired state.Overall, designing a PID controller for an automated manipulation system requires careful consideration of the system's dynamics and how it responds to changes. By carefully tuning the gain values and adjusting the components of the PID algorithm, it's possible to create a controller that effectively controls the system and meets its operational requirements.
In today's world, where technology is rapidly evolving and industries are continuously seeking to streamline their operations, automation has become an increasingly important aspect of business success. Among the various types of automation systems, one that has seen widespread adoption is the use of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) for industrial applications. These devices have revolutionized production lines, assembly lines, and other manufacturing processes by providing a reliable and efficient means of controlling complex systems with minimal human intervention. In this essay, we will explore the fundamental principles behind PLC control systems, discuss some common features of PLCs, and provide insights into how they can be used to enhance operational efficiency in various manufacturing scenarios.

One of the key features of PLCs that set them apart from traditional control systems is their ability to process real-time data from sensors and actuators within the system. This allows for rapid adjustments to the control parameters based on changing conditions, resulting in improved responsiveness and accuracy. Another significant advantage of PLCs is their flexibility, as they can be programmed to perform a wide range of functions, including monitoring, diagnostics, and predictive maintenance. This makes them ideal for a variety of industrial applications, from simple batch processing to complex supply chain management systems. Additionally, PLCs offer a high degree of security and reliability, thanks to their robust hardware and software architecture, which minimizes potential risks associated with electrical and mechanical failures.
When it comes to designing PLC systems for specific applications, there are several key considerations that must be addressed. One of the most important aspects of designing PLC-based systems is the selection of appropriate hardware components, such as microprocessors, input/output modules, and communication protocols. It is essential to choose components that are compatible with each other and meet the performance requirements of the application, while also being cost-effective and easy to install. Additionally, the choice of programming languages and development environments must be carefully considered, as well as the need for error handling and fault tolerance mechanisms to ensure the stability and reliability of the system.
Another crucial aspect of PLC design is the implementation of advanced algorithms and control strategies that take into account both short-term and long-term factors influencing system behavior. This requires a deep understanding of the underlying dynamics of the industrial process being controlled, as well as knowledge of the available control options and their trade-offs. For example, if a process is highly sensitive to temperature variations, a more sophisticated PID controller may be necessary to achieve optimal performance over time. Similarly, if a system requires frequent adjustments to compensate for changes in environmental conditions, a more adaptive or learning-based control algorithm might be more effective than a fixed PID controller.
In order to ensure that PLC designs meet the needs of their intended users, it is essential to conduct thorough testing and validation of the system. This includes testing different operational scenarios, evaluating the system's response to disturbances and errors, and verifying that all control actions are performed accurately and efficiently. Additionally, it is important to obtain feedback from users and stakeholders to identify areas where improvements can be made and refine the system further.
Despite the many benefits of using PLCs in modern manufacturing processes, there are still challenges that need to be addressed. One major issue is the complexity and interconnectivity of modern PLC networks, which can lead to issues such as miscommunications or conflicts between different systems. To address this problem, it is important to implement strict standards and protocols for communication between PLCs, and to use reliable and secure communication technologies like Ethernet or Modbus. Another challenge is ensuring that the PLC systems are scalable and flexible enough to accommodate future changes in production requirements. This requires careful planning and design at the outset, with a focus on creating modular systems that can easily be expanded or modified as needed.
In conclusion, the use of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) in modern manufacturing processes represents a critical investment in operational efficiency and productivity. By carefully selecting the right components, implementing advanced control strategies, and conducting rigorous testing and validation, manufacturers can harness the full potential of these powerful tools to drive growth and success in the global marketplace. As industry continues to evolve and demand ever higher levels of automation and precision, the importance of PLC-based solutions will only grow stronger, making them an essential component of any modern manufacturing strategy.
Content expansion reading:

Content:
Hey there! If you're new to the world of PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), or you're looking to brush up on your knowledge, understanding PLC control system wiring diagrams is a crucial step. These diagrams can seem intimidating at first, but once you know what to look for, they're actually pretty straightforward.
So, let's dive in and break down what a PLC control system wiring diagram is and how to interpret it.
First things first, a PLC control system wiring diagram is a visual representation of the electrical connections and components in a PLC system. It shows how the various parts of the system are interconnected, including the PLC itself, input devices, output devices, and any other associated equipment.
When you're looking at a PLC wiring diagram, you'll typically see a few key components:
1、PLC Unit: This is the brain of the system. It's where the programming and logic take place.
2、Input Devices: These are the sensors that provide data to the PLC. They can be switches, buttons, temperature sensors, or any other device that sends a signal to the PLC.
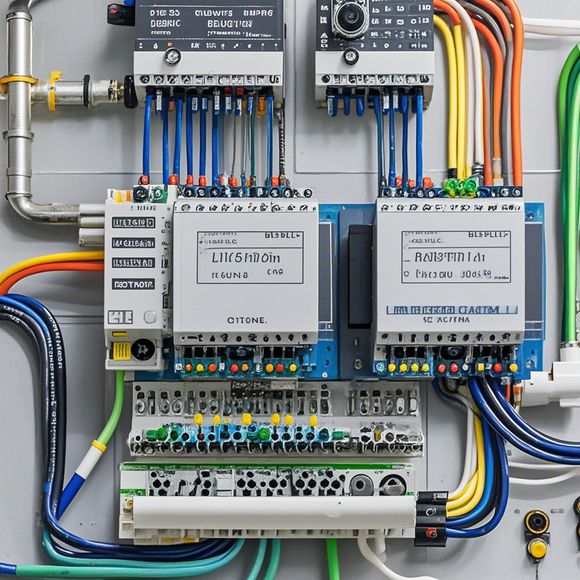
3、Output Devices: These are the devices that receive instructions from the PLC. They can be motors, lights, solenoids, or anything that needs to be controlled by the PLC.
4、Power Supplies: These provide the necessary voltage to the PLC and other components.
5、Relays and Contactors: These are switches that control power in the system.
The diagram will show how these components are connected, with lines representing the electrical connections. It's important to note that the lines in the diagram don't necessarily reflect the physical layout of the equipment; they're more concerned with the logical connections.
Here's a simplified example of what a PLC wiring diagram might look like:
PLC Unit | |
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
PLC Controller Wiring Guideline
PLC Controller for Manufacturing Automation
The cost of a PLC Controller: A Comprehensive Analysis
PLC Programming for Automation Control in the Manufacturing Industry