PLC Controllers: The Backbone of Modern Manufacturing Revolution
PLC控制器:现代制造业革命的基石。在现代制造业中,PLC控制器扮演着至关重要的角色。它们作为工业自动化的核心,通过编程和控制各种设备和机械,实现了生产效率的极大提升。PLC控制器以其强大的处理能力和灵活的控制方式,能够适应各种不同的工业环境和生产需求。无论是简单的生产线控制,还是复杂的生产流程管理,PLC控制器都能够胜任。PLC控制器还具有高度的可扩展性和可定制性,可以根据企业的特定需求进行功能定制和系统优化。PLC控制器已经成为现代制造业不可或缺的一部分,为制造业的发展提供了强大的技术支撑。
In a world where efficiency and productivity are the watchwords of modern-day business operations, the PLC controller stands out as a beacon of innovation and reliability. These sophisticated devices, which have been around for over a century, have evolved from humble beginnings to become the backbone of today's advanced manufacturing processes. As an experienced foreign trade operator, I am well aware of the critical role these controllers play in ensuring smooth and seamless production lines. In this essay, I will delve into the working principles of PLC controllers, highlighting their significance in today's global supply chain landscape.
At its core, PLC controllers operate on a principle of interfacing with various sensors and actuators to monitor and control industrial processes. This is achieved through a series of intricate electronic circuits that allow for precise data acquisition, processing, and feedback loops. By analyzing the input signals, the controller generates corresponding output signals that adjust the speed, direction, and other parameters of the machinery involved. Through this continuous monitoring and adjustment process, PLC controllers ensure that production runs smoothly and efficiently, reducing downtime and increasing overall production yield.
One of the most significant advantages of PLC controllers is their ability to automate complex tasks. With the help of advanced algorithms and software, PLCs can handle a vast range of production processes, from simple assembly lines to complex assembly lines that involve multiple stages of assembly. This automation not only reduces labor costs but also enhances product quality by minimizing human error and providing consistent results every time. Moreover, by integrating with other systems such as computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM), PLCs can create a highly efficient and flexible production system that can adapt to changing market demands.
Another critical aspect of PLC controllers is their ability to integrate with different types of hardware and software. With a wide range of input/output modules available, PLCs can interface with a variety of devices including sensors, motors, and communication networks. This integration allows for a more flexible and scalable system that can easily accommodate changes in technology or production requirements. For example, PLCs can be connected to wireless networks to enable remote monitoring and control, while they can also interface with other manufacturing systems to facilitate cross-industry collaboration.
However, the true magic of PLC controllers lies in their ability to provide real-time data analysis and decision making capabilities. By collecting and analyzing data from various sensors and actuators, PLCs can identify patterns and trends that can inform production optimization. This data-driven approach enables businesses to make informed decisions about inventory management, order fulfillment, and other critical aspects of their operations. For instance, using real-time monitoring data, manufacturers can adjust production schedules to minimize waste and optimize resource usage.
Despite their numerous benefits, PLC controllers still face some challenges in terms of cost and complexity. The initial investment in setting up a PLC system can be substantial, especially for smaller companies without extensive experience in automation. Furthermore, programming and maintenance of these controllers require specialized knowledge and expertise, which can increase operational costs over time. Nevertheless, with careful planning and investment in training, these challenges can be overcome, enabling businesses to realize the full potential of PLC controllers in enhancing their production efficiency and profitability.
In conclusion, PLC controllers represent a powerful tool for modern manufacturing industries. By seamlessly automating complex production processes, improving efficiency and productivity, and providing real-time data analysis capabilities, PLC controllers have become an essential component of any successful global supply chain. As a foreign trade operator, I am committed to leveraging the power of PLC controllers to drive growth and innovation in my industry while staying ahead of the curve in terms of technological advancements. By embracing the principles outlined above, we can unlock even greater opportunities for success in our global marketplace.
Content expansion reading:
Content:
Hey there! If you're new to the world of industrial automation or looking to refresh your knowledge on programmable logic controllers (PLCs), you've come to the right place. PLCs are the workhorses of the manufacturing industry, responsible for controlling and automating a wide range of processes. In this article, we're going to dive into the nitty-gritty of how PLCs work, so you can better understand their role in modern production systems.
First things first, let's define what a PLC is. A PLC is a digital computer designed to control and automate industrial electromechanical processes. It's like a Swiss Army knife of automation, capable of performing a variety of tasks such as switching on/off machinery, monitoring temperature, controlling motors, and much more.
At the heart of a PLC is its central processing unit (CPU), which is similar to the brain of a computer. The CPU interprets the program instructions and makes decisions based on the input it receives from various sensors and devices connected to the PLC. This input can be anything from a simple on/off switch to a complex temperature sensor.
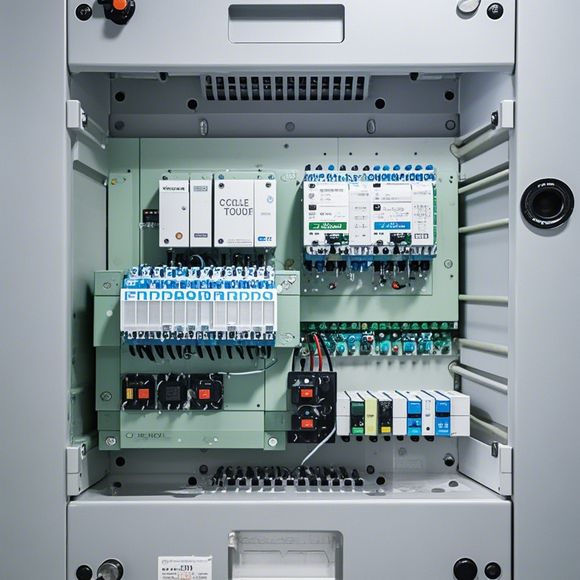

Once the CPU has processed the input data, it sends output signals to actuators, which are the devices that perform the actual tasks. For example, if a temperature sensor tells the PLC that the temperature is too high, the PLC might send a signal to an actuator to turn on a fan or adjust a valve to cool down the system.
PLCs use a variety of programming languages, such as ladder logic, which is designed to be easy for electricians and technicians to understand. Ladder logic is a graphical representation of the control logic, making it straightforward to read and troubleshoot.
One of the key benefits of PLCs is their ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously. This is thanks to their ability to scan and execute programs in a very short time, ensuring that all parts of a process are controlled in an orderly and efficient manner.
PLCs are also incredibly reliable. They're designed to operate in harsh industrial environments and can withstand temperature changes, electrical noise, and vibration. Many PLCs have built-in redundancy features, such as dual power supplies or multiple CPUs, to ensure continuous operation even if one component fails.
In terms of scalability, PLCs can be easily expanded to accommodate more inputs and outputs as a process grows. This modular design allows for the addition of more modules, such as analog input/output modules, discrete input/output modules, or specialty modules like communication or motion control.
When it comes to communication, PLCs can talk to a variety of devices and systems. They can connect to human-machine interfaces (HMIs) for operator interaction, other PLCs in a network, or even enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems for integration with business processes.
Maintenance of PLCs is also relatively straightforward. Most modern PLCs have built-in diagnostics and troubleshooting features that can help identify issues quickly. This reduces downtime and ensures that any problems can be resolved efficiently.
In conclusion, PLCs are the backbone of industrial automation, offering a flexible, reliable, and scalable solution for controlling and automating a wide range of processes. Whether you're in the manufacturing, energy, or any other industry that involves complex control systems, understanding how PLCs work is essential for effective operation and maintenance.
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
PLC Programming for Automation Control in the Manufacturing Industry
How to Use a PLC Controller for Your Business
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations
Connecting a PLC Controller to Your Computer
PLC Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Their Prices