Introduction to the PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Controller
Hello everyone! Today, I'd like to talk about the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC). It’s a device that can be programmed to control various industrial processes. It has been around for decades and is widely used across various industries. PLCs are great because they allow for precise and reliable control of machines and equipment. They can handle a wide range of tasks, from simple automation to complex production lines. So next time you have a question about how to program or use PLCs, feel free to ask me.
In this age of technological advancements, the role of automation in manufacturing and industrial processes becomes increasingly crucial. One such technology that has revolutionized many industries is Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). These versatile controllers are designed to automate a wide range of industrial processes, from simple machine control to complex systems involving multiple sensors and actuators. In this essay, we will delve into the world of PLCs, exploring their fundamental working principles, functionalities, applications, and future prospects.
At its core, a PLC is an intelligent device that performs a specific task based on pre-defined instructions or commands stored in its memory. It operates on a microprocessor system that executes these instructions in real-time, allowing it to respond quickly to changes in the environment. The PLC communicates with other devices in the industrial network through a variety of protocols such as Profibus, Ethernet, or IEPE.
One of the key features of PLCs is their flexibility and adaptability. They can be programmed to perform a wide range of tasks, from simple logic control to complex simulations and simulations. This flexibility allows PLCs to be tailored to the specific needs of different industries, making them ideal for use in various sectors such as manufacturing, energy production, transportation, and more.
The functionality of a PLC controller can be broadly categorized into three main functions: input/output processing, logic control, and communication. Firstly, the input/output processing function allows the PLC to read data from sensors and output control signals to actuators. This enables the PLC to monitor and manipulate physical processes in real time, providing valuable feedback to the operator. Secondly, the logic control function allows the PLC to process data based on pre-set rules or algorithms. This can include things like temperature control in a furnace, or sequencing of steps in a robotic assembly line. Lastly, the communication function allows the PLC to interact with various types of devices, including PCs, workstations, and external hardware, facilitating data exchange and remote monitoring.
One of the most common applications of PLCs is in the field of industrial control systems. In these systems, the PLC serves as the brain behind the operation of machines, automating processes and ensuring they run efficiently and reliably. For instance, in a manufacturing plant, the PLC could be responsible for controlling the speed at which conveyor belts transport parts, adjusting the temperature of ovens during baking cycles, or even monitoring the quality of products being produced.
Another important application of PLCs is in the area of automation in transportation systems. Vehicles equipped with PLCs can be used to control everything from fuel delivery to tire pressure checks, reducing downtime and improving safety. Furthermore, the integration of PLCs with Internet of Things (IoT) technologies allows for even greater automation and connectivity, enabling vehicles to communicate with one another and with traffic management systems.
In addition to their applications in industrial and transportation settings, PLCs also have a significant role in the field of renewable energy. For example, in solar power plants, PLCs can be used to control the flow of water and electrical energy to the panels, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing wastage. Similarly, in wind farms, the PLC can be used to monitor and manage the operation of turbines, ensuring safe and reliable operation while maximizing efficiency.
Despite their numerous benefits, there are challenges associated with using PLCs that must be addressed to ensure their continued success in various industries. One such challenge is software development, where the complexity of programming can make it difficult for non-technical users to effectively manage and maintain PLC systems. To address this issue, many manufacturers offer comprehensive training and support services to help users understand and operate their PLCs effectively.
Another potential obstacle to the adoption of PLCs is the need for skilled technicians who can maintain and troubleshoot these systems effectively. As the complexity of PLCs increases, so too does the demand for skilled professionals who can handle the technical details involved in maintaining these devices. Therefore, investing in training programs and providing access to qualified technicians may be necessary to ensure the long-term success and reliability of PLC-based systems.
As technology continues to evolve, the potential for PLCs to expand their capabilities remains enormous. For instance, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning may allow these controllers to learn and adapt over time, enhancing their performance in real-world scenarios. Additionally, advancements in wireless communication technologies may enable PLCs to communicate seamlessly with other systems, creating new opportunities for automation and optimization across various industries.
In conclusion, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) play a vital role in modern industrial and transportation systems by automating processes and ensuring reliable operation. With their flexibility and adaptability, PLCs can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different industries, making them an essential tool for businesses around the world. As technology continues to advance, the potential for PLCs to expand their capabilities remains vast, offering endless possibilities for innovation and progress in the field of automation.
Content expansion reading:
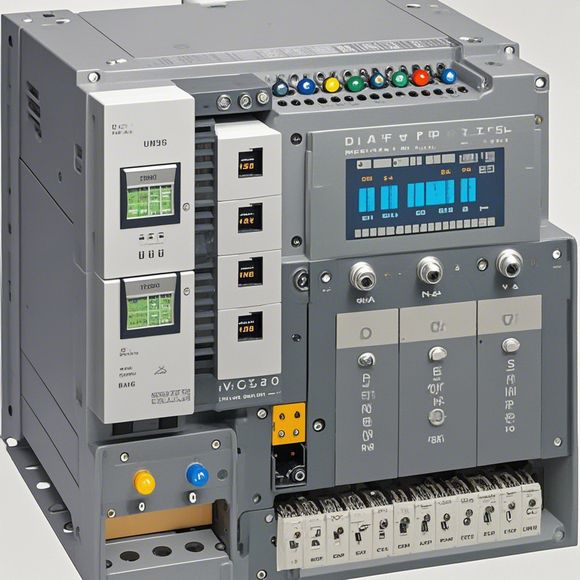

Content:
Hey there! Today, we're diving into the world of Programmable Logic Controllers, or PLCs for short. These bad boys are the workhorses of automation, controlling a wide range of industrial processes. But how do they actually work? Let's break it down in a way that's easy to understand, even if you're new to the world of PLCs.
Imagine you're running a factory and you have a bunch of machines that need to work together in a specific order. That's where PLCs come in. They're like the conductor of an orchestra, making sure that everything happens when it's supposed to, and that everything is running smoothly.
At the heart of a PLC is a microprocessor, which is kind of like the brain. This brain takes in information from various sensors and switches around the factory. These inputs could be anything from a button being pressed to a temperature reading. The PLC then uses this information to decide what to do next.
Once the PLC has all the input data, it compares it to a set of pre-programmed instructions. These instructions are like a recipe for the PLC to follow. They tell the PLC what to do in response to the inputs it's received. For example, if a temperature sensor reads too high, the PLC might tell a valve to open and let more coolant into the system.
The output side of the PLC is where the decisions made by the microprocessor are carried out. This is usually through controlling actuators, which are devices that can do something in the real world, like open a valve or start a motor. The PLC tells these actuators what to do based on the program it's been given.
PLCs are super flexible because you can change the program in them to suit different tasks or processes. This means that one PLC could be used in a variety of factories, just by changing the instructions it follows. It's like having a Swiss Army knife of automation.
One of the key benefits of PLCs is their reliability. They're designed to operate 24/7 in tough industrial environments. They can handle a lot of wear and tear and are built to last. Plus, they're generally very safe, with built-in features to prevent accidents and protect workers.
In summary, PLCs are all about taking in data, making decisions based on that data, and then acting on those decisions to control various systems. They're the backbone of automation, ensuring that complex processes run efficiently and safely. Whether you're in manufacturing, oil and gas, or any other industry that involves automation, PLCs are the go-to solution for keeping things running smoothly.
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
PLC Programming for Automation Control in the Manufacturing Industry
How to Use a PLC Controller for Your Business
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations
Connecting a PLC Controller to Your Computer
PLC Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Their Prices