PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Wiring End-Points Explanation
Sure, I'm happy to provide a brief summary of what you've mentioned in your content.PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Wiring End-Points Explanation:The PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is an essential tool for automation and industrial control systems. Its primary function is to process and analyze the data collected from various sensors and devices, then execute commands accordingly. To achieve this, the PLC needs to communicate with various end-points through wiring.Wiring is the method used to connect the PLC to these end-points. The end-points can be anything from sensors, valves, motors, or other control devices. Each end-point requires specific electrical connections to the PLC, which are known as wiring points. These points are crucial in ensuring that the PLC can receive and send signals accurately.There are different types of wiring, including direct wiring, hybrid wiring, and distributed wiring. Direct wiring involves connecting one end-point directly to the PLC. Hybrid wiring combines direct wiring with distributed wiring by using cables to connect multiple end-points to the PLC. Distributed wiring involves connecting multiple end-points to a centralized location, usually at the factory or control room, where they can be easily managed and monitored by the PLC.In summary, PLC wiring end-points refer to the electrical connections made between the PLC and various control devices, ensuring efficient communication and control over the industrial system.
Hello, everyone! Today, as your friendly and experienced sales and technical representative, I will walk you through the intricacies of the end points of a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC), also known as Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC). These wiring points are the lifelines that connect various components within the PLC to communicate effectively with each other. Let's dive into the world of PLC end-points!
Firstly, let's talk about the basics of PLC end-points. An end point is a physical connection between the PLC and its surrounding environment, allowing it to receive inputs or send outputs. These end points can be categorized based on their purpose:
1、Input End Points: These are the connections where data from external sources is received by the PLC. They come in two main types - open-wired and shielded wired. Open-wired end points use uninsulated wires to allow for direct contact with external sensors and switches. Shielded wired end points, on the other hand, are encapsulated and protected by an electrically conductive shield, making them ideal for sensitive signals like EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) protection.
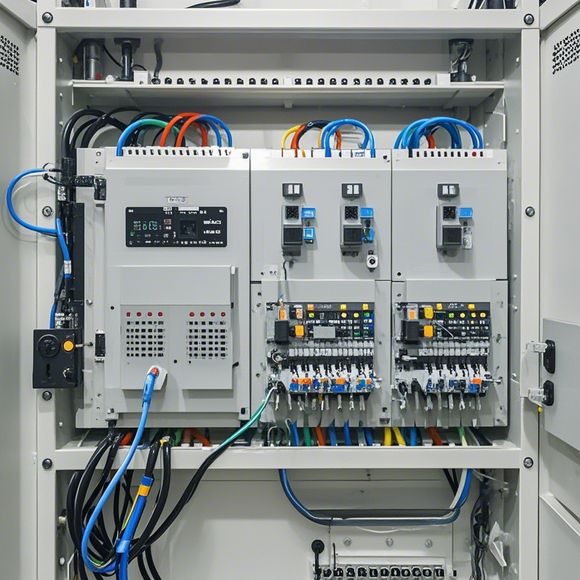

2、Output End Points: These are the connections where the PLC sends out signals to external devices such as motors, relays, or LED lights. There are several different types of output end points depending on the power level required:
- Low-power outputs: These are suitable for low-current, low-voltage applications like relays or LEDs. They have a small pin count (usually less than 16) and are typically labeled with a "L" or "H" symbol on the end point.
- Medium-power outputs: These are designed for medium-level currents and voltages, commonly used for motor control. They have a larger pin count (usually 16 or more) and are often labeled with letters indicating their function - M for Motor, T for Transmitters, etc.
- High-power outputs: These handle high-current and high-voltage signals, suitable for high-intensity loads like fans or heaters. They also have a large number of pins (usually over 20) and are usually marked with a "H" or "S" symbol to indicate their function.
Now let's delve deeper into how these end points are connected and what they do:
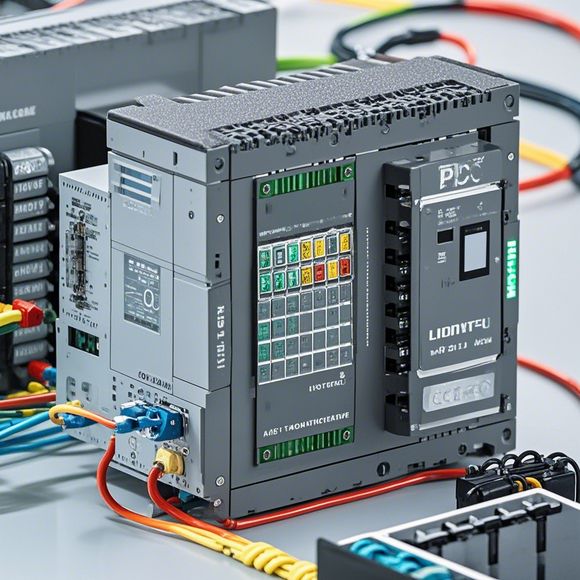

When designing a PLC system, it's important to understand how end points are arranged and wired. This involves selecting appropriate connectors, cables, and connectors based on the type and size of end points, as well as the power requirements of the components being controlled. Here's a quick look at how this process works:
1、Wire Diagram Design: The first step is creating a wire diagram that shows all the connections between the different end points. This diagram helps visualize the overall layout of the PLC network and ensures that all components are properly connected.
2、Connectors and Cables: Once the wire diagram is complete, the next step is selecting the appropriate connectors and cables for each end point. Connectors should match the specifications of the end points and ensure a secure and reliable connection without any short circuits. Cables should be long enough to reach all the required locations, but not so long as to cause issues with installation or maintenance.
3、Installation: Finally, once all the connectors and cables have been installed, the PLC is tested to ensure that all connections are working correctly. This includes verifying that the input end points receive the correct signals, and the output end points send signals to the appropriate destinations.
4、Maintenance: In addition to regular testing, it's important to perform periodic maintenance on the PLC network to identify and fix any potential problems before they become more serious. This includes checking for corrosion, loose connections, or damaged cables.
In summary, understanding the end points of a PLC is crucial for maintaining a healthy and reliable network. By following the steps outlined above, you can confidently install and maintain your PLC network, ensuring that your devices are communicating efficiently and reliably. Remember, proper planning and attention to detail are key to a successful PLC project!
Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
PLC Programming for Automation Control in the Manufacturing Industry
How to Use a PLC Controller for Your Business
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Control System Basics
Plumbers Rule! The Role of PLC Controllers in the World of Waterworks
PLC Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Their Prices