PLC Controllers - The Powerful Backbone of Modern Industrial Automation
PLC控制器在现代工业自动化中扮演着至关重要的角色。它们通过实时控制和数据处理功能,实现了对生产过程的精确监控和管理。PLC控制器的应用范围非常广泛,涵盖了从简单的逻辑控制到复杂的过程优化等多个领域。在制造业中,PLC控制器可以实现生产线的自动化控制,提高生产效率和产品质量;在能源领域,它们可以用于智能电网的控制和管理,实现能源的有效利用和分配。PLC控制器已经成为现代工业自动化不可或缺的一部分,它们的强大功能和广泛应用为工业生产带来了革命性的变化。
In the realm of industrial automation, the presence of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) is akin to the heartbeat of any modern manufacturing plant or industrial facility. These controllers serve as the backbone of a system that allows for precise control over a wide range of processes and equipment, from simple conveyor belts to complex assembly lines.
At their core, PLCs are designed to process data and instructions in real-time, allowing them to respond quickly and effectively to changes in conditions or commands. They can be programmed with a variety of algorithms, logic functions, and user-defined routines, enabling them to handle an almost infinite number of tasks.
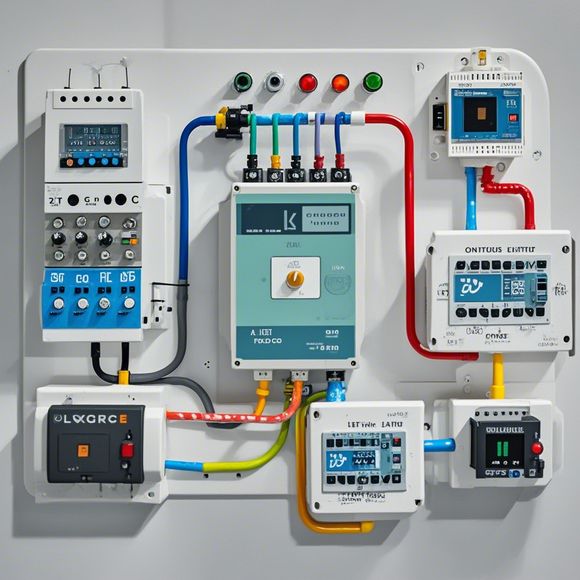

One of the key advantages of PLCs is their modular design, which allows them to be easily expanded or replaced without having to completely rewire the system. This flexibility makes them ideal for use in environments where changes in production or operational requirements may occur frequently.
Another critical aspect of PLCs is their ability to communicate with other devices and systems within the plant network. By integrating with sensors, switches, and other control units, PLCs can provide comprehensive feedback loops that help maintain optimal performance levels across the entire system.
The reliability and robustness of PLCs are also unrivaled. They are designed to withstand high levels of temperature and humidity, as well as shock and vibration, making them suitable for use in harsh environments where traditional hardware may not be able to operate effectively.
In addition to these technical benefits, PLCs offer significant economic advantages as well. With their ability to automate complex processes and minimize downtime, they can help reduce operating costs and increase overall profitability. Additionally, by reducing the need for manual intervention, PLCs can free up valuable human resources for more strategic and creative work.
Of course, like any technology, there are some potential drawbacks to consider when using PLCs. For example, while they are highly reliable, they can still fail due to issues such as software bugs or hardware defects. However, by regularly monitoring and maintaining them, these problems can be quickly detected and addressed before they cause serious disruptions.
Overall, the role of PLCs in modern industrial automation cannot be overstated. As the heart of many complex systems, they continue to evolve and improve, offering new capabilities and solutions at each iteration. Whether you're a small business owner looking to streamline your operations or a large corporation seeking to stay ahead of the competition, investing in quality PLC controllers is a smart decision that will pay dividends for years to come.
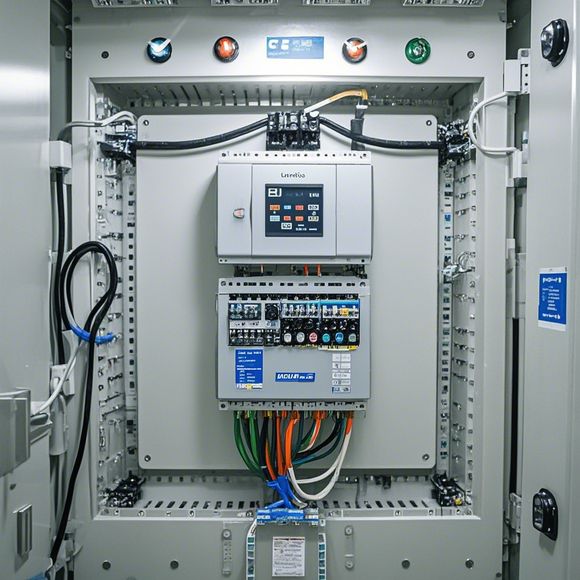

Content expansion reading:
Content:
Hey there! If you're new to the world of industrial automation or looking to refresh your knowledge on programmable logic controllers (PLCs), you've come to the right place. PLCs are the workhorses of the manufacturing industry, responsible for controlling and automating a wide range of processes. In this article, we're going to dive into the nitty-gritty of how PLCs work, so you can better understand their role in modern production systems.
First things first, let's define what a PLC is. A PLC is a digital computer designed to control and automate industrial electromechanical processes. It's like a Swiss Army knife of automation, capable of performing a variety of tasks such as switching, timing, counting, and sequencing. PLCs are known for their reliability, durability, and ability to operate in harsh environments.
At the heart of a PLC is its central processing unit (CPU), which is essentially the brain of the system. The CPU interprets the program instructions stored in its memory and makes decisions based on the input it receives from various sensors and switches. This input can be anything from simple on/off signals to more complex analog data.
The program that the PLC runs is written in a special language designed for industrial control, such as ladder logic, function block diagram, or more recently, structured text. Ladder logic is the most common and it's based on the relay logic used in traditional electromechanical control systems. It's a visual programming language that uses graphical symbols to represent the logic of the system.
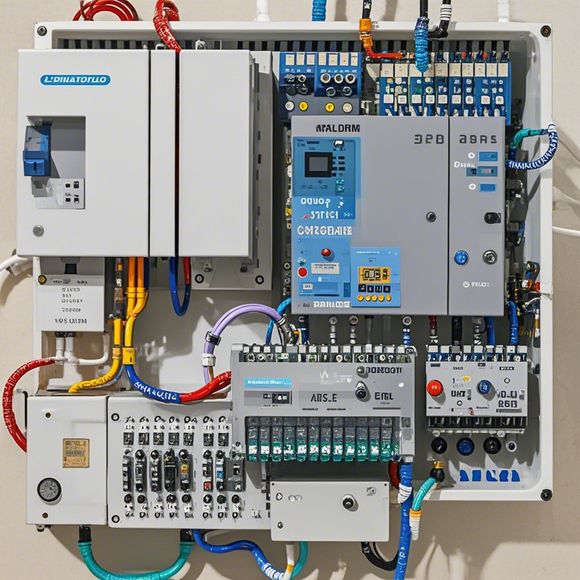
Once the program is written and downloaded into the PLC, it's ready to start receiving input from the field devices connected to it. These devices can include limit switches, temperature sensors, pressure transducers, and many more. The PLC then processes this input according to the program and outputs the necessary control signals to actuators like motors, valves, and lights.
The cycle of input, processing, and output is continuous, with the PLC executing the program in a loop at a very high speed. This allows for real-time control of the process, ensuring that it operates efficiently and safely.
PLCs are also known for their modular design, which means they can be easily expanded with additional input/output (I/O) modules as the control needs of a system grow. These modules can be analog or digital, depending on the type of data they handle.
One of the key benefits of PLCs is their ability to handle complex control tasks that would be impractical or impossible for a human operator to perform. They can manage multiple tasks simultaneously, respond to changes in the process quickly, and operate around the clock with very little downtime.
In summary, PLCs are essential components of industrial automation, providing a flexible and reliable means of controlling various processes. Their ability to interpret complex programs and respond to inputs quickly makes them indispensable in modern manufacturing environments. Whether you're a seasoned pro or just starting out, understanding the basics of PLCs is crucial for anyone involved in industrial operations.
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
PLC Controller Selection Guide for Foreign Trade Operations
PLC Controller Wiring Guideline
PLC Controller for Manufacturing Automation
The cost of a PLC Controller: A Comprehensive Analysis
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Control System Basics
Plumbers Rule! The Role of PLC Controllers in the World of Waterworks