PLC Control Systems Overview
Sure, I'd be happy to provide an overview of PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Control Systems.PLC systems are used to control and monitor processes in industrial settings. They can be programmed with algorithms or routines to automate specific tasks, such as controlling a machine's speed or adjusting the flow of materials.One of the key advantages of PLC systems is their flexibility. They can be easily configured to meet specific industrial needs, whether for simple tasks like lighting or more complex ones like temperature regulation or process automation. Additionally, PLCs offer robust security features to prevent unauthorized access and ensure the safe operation of the system.Overall, PLC control systems have become increasingly popular in industries around the world due to their ability to simplify complex control tasks and improve efficiency.
Introduction to PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers) Control Systems:
A PLC is a versatile and powerful device that plays an integral role in modern industrial environments. It stands for "Programmable Logic Controller," and it's the brain behind many complex automation processes. The PLC system consists of hardware components such as input/output interface boards, programmable logic units, and communication modules, and software that manages these components to execute predefined logic and control functions.
The PLC is designed to work with standardized electrical signals and data formats, enabling it to communicate seamlessly across various devices and networks. Its key advantage over other types of controllers lies in its ability to be customized to specific applications, making it highly flexible in meeting the needs of different industries.
The heart of the PLC is its Programmable Logic Unit, which contains all the logic and algorithms that dictate how the PLC operates. This unit is typically housed within a compact enclosure, which also serves as the PLC's memory storage area. The programming software allows you to define the sequence of instructions that will be executed when the PLC is activated.
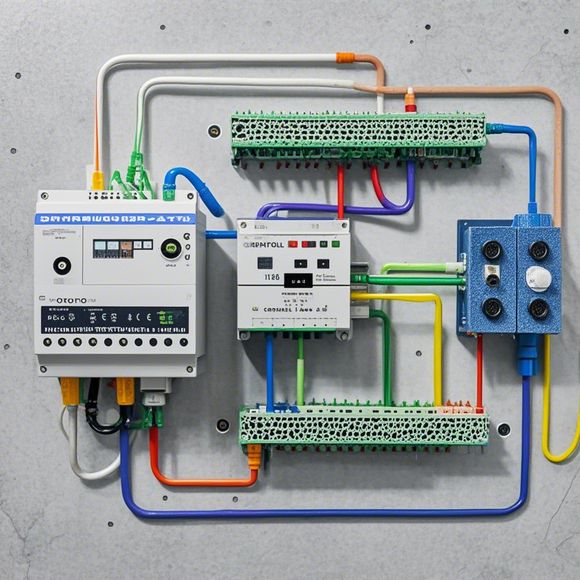
Communication between the hardware and software components of the PLC is facilitated by input/output interface cards or modules. These are used to connect external sensors, actuators, and other devices to the control system. They also serve as a conduit for sending and receiving data between the PLC and other systems in the network.
PLCs can be categorized based on their complexity and intended use. Simple models may only handle basic operations, while more advanced models can perform complex calculations and process real-time data from sensors. They can also be divided into two main types: field-bus-based and non-field-bus-based PLCs. Field-bus-based systems are more common in industry and offer better connectivity with other devices in the manufacturing plant. Non-field-bus-based systems are simpler to install and use, but they require additional wiring and configuration.
In addition to hardware and software integration, PLCs are often integrated with other technologies like HMIs (Human Machine Interfaces), SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition) systems, and even cloud computing services. These technologies enhance the overall functionality of the PLC system, providing users with access to real-time monitoring, data analysis, and predictive maintenance capabilities.
One of the most significant advantages of PLCs is their ability to automate complex production processes. By using PLCs in manufacturing plants, companies can reduce labor costs, streamline operations, and improve overall efficiency. Additionally, PLCs can handle high levels of precision and reliability when controlling machinery and equipment, which is crucial in sectors like automotive engineering, medical technology, and pharmaceuticals.
Another critical application of PLCs is in industrial safety systems. In these systems, PLCs monitor critical parameters like temperature, pressure, and flow rate, ensuring that the manufacturing process remains safe and under control. They can detect anomalies early on and take action before any accidents occur, ultimately reducing potential damage and saving lives.
Finally, PLCs have made significant strides in the field of renewable energy generation. By automating the operation of wind turbines and solar panels, PLCs help to maximize energy production and minimize downtime. This not only reduces operational costs but also contributes significantly to sustainable development goals worldwide.
In conclusion, the PLC control system is an essential tool in modern industries. Its flexibility and adaptability make it a reliable and efficient solution for managing complex automation processes. Whether you're looking to automate simple tasks or optimize entire production lines, a PLC can help you achieve your goals with ease. As technology continues to advance, we can expect the PLC to become increasingly intelligent and capable of performing even more sophisticated functions.
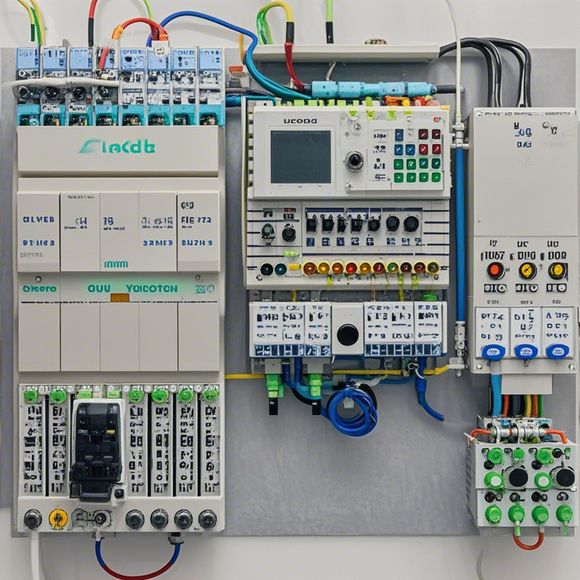

Content expansion reading:
Content:
Hey there! If you're new to the world of PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), or you're looking to brush up on your knowledge, understanding PLC control system wiring diagrams is a crucial step. These diagrams can seem intimidating at first, but once you know what to look for, they're actually pretty straightforward.
So, let's dive in and break down what a PLC control system wiring diagram is and how to interpret it.
First things first, a PLC control system wiring diagram is a visual representation of the electrical connections and components in a PLC system. It shows how the various parts of the system are interconnected, including the PLC itself, input devices, output devices, and any other associated equipment.
When you're looking at a PLC wiring diagram, you'll typically see a few key components:
1、PLC Unit: This is the brain of the system. It's where the programming and logic take place.
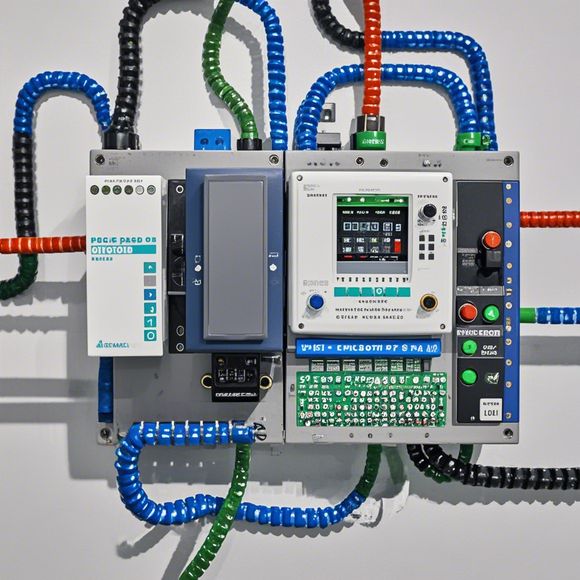
2、Input Devices: These are the sensors that provide data to the PLC. They can be switches, buttons, temperature sensors, or any other device that sends a signal to the PLC.
3、Output Devices: These are the devices that receive instructions from the PLC. They can be motors, lights, solenoids, or anything that needs to be controlled by the PLC.
4、Power Supplies: These provide the necessary voltage to the PLC and other components.
5、Relays and Contactors: These are switches that control power in the system.
The diagram will show how these components are connected, with lines representing the electrical connections. It's important to note that the lines in the diagram don't necessarily reflect the physical layout of the equipment; they're more concerned with the logical connections.
Here's a simplified example of what a PLC wiring diagram might look like:
PLC Unit | |
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The cost of a PLC Controller: A Comprehensive Analysis
PLC Programming for Automation Control in the Manufacturing Industry
Connecting a PLC Controller to Your Computer
Effective Strategies for Handling PLC Control System Faults
What is a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
PLC Controller Advantages: A Comprehensive Guide for Success in Global Trade