The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Modern Manufacturing
In the modern age of manufacturing, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) have become indispensable components. These devices are responsible for managing and coordinating complex industrial processes, ensuring efficiency and productivity. PLCs are highly flexible and can be customized to suit a wide range of applications, making them an essential tool for modern manufacturing industries. Their ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously allows for greater flexibility in production lines, while their reliability ensures consistent quality output. As automation becomes increasingly important in today's world, the role of PLCs cannot be overstated, providing critical support for modern manufacturing operations.
In the world of manufacturing, where efficiency and precision are paramount, the importance of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) cannot be overstated. These advanced digital controllers play a crucial role in automating processes, enhancing productivity, and ensuring consistent quality output. As we dive deeper into the realms of industrial automation, it is essential to understand what makes PLCs so integral to modern manufacturing operations. In this essay, we shall delve into the various facets that make these marvels of engineering stand out from traditional control systems.
Firstly, let's explore the concept of PLCs. At its core, a Programmable Logic Controller is a versatile device designed to perform complex calculations and logical operations based on programmed instructions. Unlike traditional mechanical or electro-mechanical controllers, PLCs can be reprogrammed with minimal hardware replacement, making them highly adaptable to changing production needs. This inherent flexibility is what sets PLCs apart in an industry where speed, accuracy, and reliability are key performance indicators.
One critical aspect of PLC functionality is their ability to communicate with various types of sensor inputs and actuator outputs. By integrating with motion control systems, process control systems, and other automation components, PLCs create a cohesive system that responds to changes in real-time. For instance, if a machine tool detects an irregularity in a part being processed, the PLC could immediately adjust the cutting parameters to compensate for the deviation, ensuring flawless product quality. Such proactive monitoring capabilities are unparalleled by conventional feedback loops, which often rely on retrospective analysis of past data.
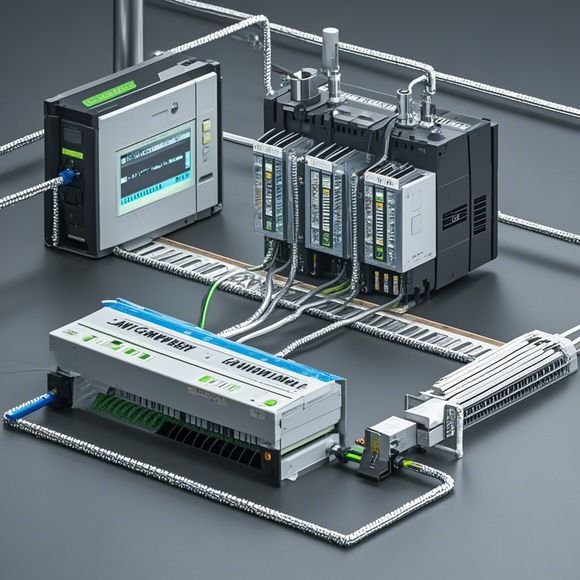
Furthermore, the programming language employed by PLC manufacturers varies significantly from one manufacturer to another. However, most common languages include ladder logic, function blocks, and structured text. The choice of language ultimately depends on the specific needs of the user and the complexity of the automation tasks at hand. Ladder logic, for example, is ideal for simple sequences of operations, while more complex tasks might require the use of function blocks or structured text. Regardless of the chosen programming language, the key is to ensure that the code adheres to best practices and follows the manufacturer's guidelines to avoid potential errors or unexpected behavior.
Another important aspect of PLCs is their ability to integrate with existing IT infrastructure. Many modern PLCs come equipped with Ethernet connectivity, allowing them to connect directly to servers, storage devices, and cloud services. This integration not only enhances the user experience by providing real-time data access but also enables remote monitoring and maintenance, saving valuable time and effort. For example, when a PLC detects anomalies during production, the relevant data can be transmitted instantly to a centralized database for analysis and decision-making.
In addition to their technical benefits, the adoption of PLCs in manufacturing has significant economic implications. By reducing downtime and increasing production rates, PLCs have the potential to save businesses substantial amounts of money. Moreover, they offer cost savings by eliminating the need for costly manual labor or outdated machinery that may not meet modern production standards. Furthermore, by streamlining processes and improving efficiency, PLCs can help companies reduce waste and increase profitability.
When it comes to selecting PLCs, several considerations must be made. Firstly, the user should assess their specific application requirements, including the number and type of input/output devices, as well as the desired programming language and connectivity options. Next, it's essential to evaluate the available features, such as high-speed processing capabilities, memory capacity, and error handling mechanisms. Finally, cost-effectiveness should not be overlooked; however, it's equally important to consider the long-term value of the investment in terms of increased productivity and reduced operational expenses.
Another important aspect of PLC selection is their compatibility with existing systems. While many PLCs are designed to work seamlessly with existing automation hardware and software, it's crucial to ensure that the chosen solution will fit seamlessly within the company's existing infrastructure. This involves considering factors such as power supply requirements, communication protocols, and interface standards. By carefully planning and testing before deployment, businesses can minimize the risk of complications and maximize the benefits of their investment.
In conclusion, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) represent a transformative force in the world of manufacturing. With their ability to automate processes, optimize performance, and enhance overall efficiency, they have become essential tools for modern industrial operations. Whether used in small workshops or large factories, PLCs offer a range of advantages that make them a valuable asset for any business seeking to improve its competitive edge. As we continue to embrace the innovations brought forth by PLC technology, the potential to revolutionize the way we produce and manufacture goods will undoubtedly remain a powerful driving force for growth and success.
Content expansion reading:
Content:
Hey there! If you're new to the world of industrial automation, you might have come across the term "PLC controller" and wondered what it's all about. Don't worry, I'm here to break it down for you in a way that's easy to understand.
So, what is a PLC controller? PLC stands for Programmable Logic Controller. It's a type of industrial computer designed to control and automate various processes. Imagine a brain for machines and equipment. PLCs are super versatile and can be found in all sorts of industries, from manufacturing and automotive to food and beverage processing.
Here's a quick rundown of how a PLC works:
1、Inputs: These are the sensors that gather data from the environment or the process. They could be switches, buttons, temperature sensors, or any other type of device that provides information to the PLC.
2、Programming: Before a PLC can do its job, it needs to be programmed. This is where the logic comes in. Programmers use Ladder Logic, which is a graphical programming language that looks like electrical ladder diagrams, to tell the PLC what to do based on the input data.
3、CPU (Central Processing Unit): This is the heart of the PLC. It's where the program is executed, and decisions are made based on the input data. The CPU processes the information and decides whether to turn on or off outputs based on the programmed logic.
4、Outputs: These are the devices that the PLC controls. They can be motors, lights, valves, or any other equipment that needs to be turned on or off in response to the inputs and the programmed logic.
PLCs are known for their reliability, robustness, and ability to operate in harsh industrial environments. They're also designed to be easily reprogrammed, which means they can be adapted to new processes or changes in existing ones without too much hassle.
Now, let's talk about why PLCs are so popular:
Flexibility: With PLCs, you can automate a wide range of tasks and processes. Whether it's controlling a conveyor belt, monitoring temperatures, or managing a complex production line, PLCs can handle it all.
Efficiency: PLCs can make processes more efficient by ensuring that everything runs smoothly and consistently, reducing the risk of errors and improving overall productivity.
Safety: Many PLCs are designed with safety features that can prevent accidents and protect both workers and equipment.
Remote Monitoring: Modern PLCs can be connected to networks, allowing for remote monitoring and control. This means you can troubleshoot and make adjustments from anywhere in the world.
Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment in a PLC system might seem high, the long-term savings in labor, reduced downtime, and improved product quality can be significant.
So, there you have it! A PLC controller is a powerful tool that's essential for industrial automation. It's a bit like a Swiss Army knife of the automation world, capable of handling a variety of tasks with precision and reliability. Whether you're looking to automate a small process or manage a large-scale industrial operation, PLCs are definitely worth considering.
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Smart Manufacturing Solutions with PLC Integrated Machinery
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Control System Basics
Plumbers Rule! The Role of PLC Controllers in the World of Waterworks
PLC Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Their Prices