plc控制器工作原理
PLC控制器工作原理,实现自动化控制的关键技术,1. PLC简介,- 定义与发展历程,- PLC主要应用领域,- PLC与其他自动化系统比较,2. PLC基本结构,- 核心组成部分介绍,- PLC内部存储和处理机制,- 输入/输出模块功能,3. 编程与控制逻辑,- 编程语言种类及选择,- 逻辑运算与指令集详解,- 顺序控制与实时性实现,4. PLC在工业自动化中的应用案例,- 制造业自动化改造实例,- 交通运输控制系统应用,- 建筑自动化领域应用,5. 技术优势与发展趋势,- PLC与传统控制方式比较,- 高可靠性与扩展性特点,- 未来发展方向与新技术,
"Introduction to Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): The Art of Automation"
In today's highly competitive world of manufacturing and industrial automation, the importance of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) cannot be overstated. These advanced control systems have revolutionized the way industries operate by providing a reliable and efficient means of managing complex workflows. Whether you're looking to automate simple assembly lines or complex production processes, understanding the intricacies of PLCs is essential. In this guide, we'll delve deeper into the world of PLCs, exploring their key components, functionalities, benefits, and practical applications.
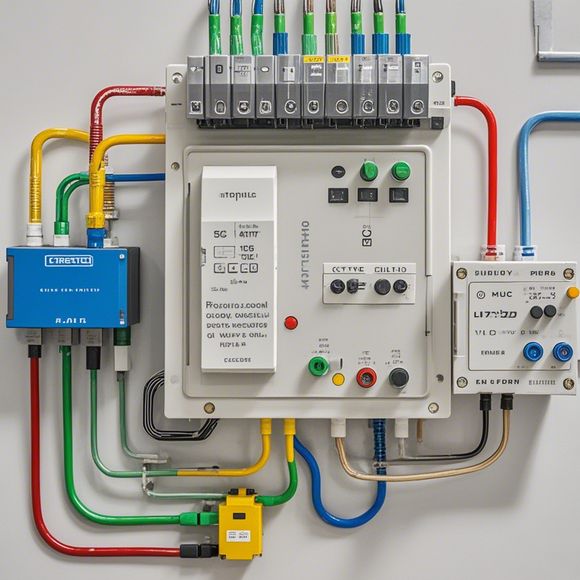
At its core, a Programmable Logic Controller operates on the principle of interfacing with digital input signals, processing them through a series of logic operations, and then outputting corresponding signals to actuate physical devices such as switches, motors, or sensors. The PLC takes the form of a microcomputer that can be programmed to perform specific tasks based on inputs from various sensors and actuators. This flexibility allows for the creation of complex control systems that can adapt to changing conditions and optimize production efficiency.
One of the defining features of PLCs is their modular architecture. Each module in a PLC system consists of a variety of specialized units, including processors, memory, input/output (I/O) modules, communication interfaces, and power supplies. These modules work together to create a complete system capable of handling a wide range of tasks, from simple logic control to complex real-time monitoring and diagnostics.
When it comes to functionality, PLCs are designed to handle a broad spectrum of industrial processes. They can monitor temperature, pressure, flow rates, and other parameters in real-time, making them ideal for process control applications such as chemical plants, food production facilities, and pharmaceutical labs. Additionally, PLCs can perform mathematical calculations using stored program instructions, which enables them to make decisions based on data analysis and predictive analytics.
Another critical benefit of PLCs is their high reliability and robustness. Thanks to modern manufacturing techniques, these controllers are built to withstand harsh operating conditions and environmental factors, ensuring long-term performance without frequent maintenance or repairs. Moreover, they feature a wide range of safety features, including automatic shutdown capabilities when certain conditions are detected, which further enhances their safety record in critical applications.
Practical applications of PLCs are equally diverse, spanning across a wide range of industries. In the automotive industry, PLCs are used to control vehicle suspension systems, tire inflation, and engine management, among other functions. In manufacturing, they are instrumental in streamlining supply chain logistics, reducing downtime due to machine failures, and improving product quality through precise control of production parameters. Furthermore, in the energy sector, PLCs play a crucial role in power generation and distribution systems, ensuring safe and efficient operation of power grids.
To truly appreciate the potential of PLCs, it's important to consider their impact on productivity and efficiency levels. By automating routine tasks and replacing human labor with more precise and accurate controls, PLCs can significantly reduce operational costs and improve overall production yields. This is particularly evident in industries where manual errors or delays can lead to lost time and revenue.
In addition to their economic benefits, PLCs offer numerous advantages in terms of safety and environment protection. They eliminate the risk of human error in hazardous environments, reducing the risk of accidents caused by human negligence. Furthermore, by controlling energy usage and minimizing waste, PLCs contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable development practices.
As technology continues to advance, the field of PLCs will continue to evolve, introducing new features and capabilities that will enable even greater automation and efficiency gains. For example, advancements in wireless communication technologies could allow for remote monitoring and control of PLC systems, making them even more flexible and adaptive in their application.
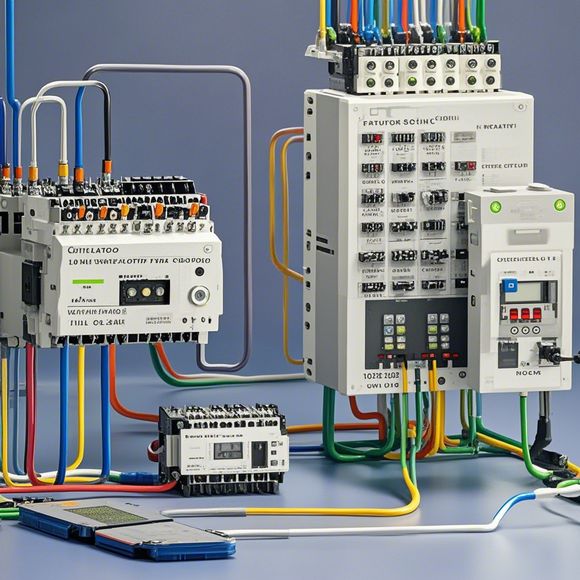

In conclusion, Programmable Logic Controllers represent an essential tool in today's modern workplace. With their ability to handle complex tasks, high reliability, and wide range of applications, they have become a cornerstone of industrial automation. As we look towards a future dominated by intelligent machines and advanced technologies, the role of PLCs will only become more significant, driving innovation and driving efficiency forward. So if you're looking to stay ahead of the curve in your industry, investing in the power of PLCs is a no-brainer.
Content expansion reading:
Content:
Hey there! Welcome to our dive into the world of Programmable Logic Controllers, or PLCs for short. If you're new to the game or just looking to refresh your knowledge, you've come to the right place. We're going to break down the basics of PLCs in a way that's easy to understand, even if you're not an electrical engineer. So, let's get started!
First things first, what exactly is a PLC? Well, it's a type of industrial controller that's designed to operate electromechanical processes. These can range from simple tasks like turning on a light to complex operations in factories, machines, and even homes. PLCs are like the brain of the operation, receiving input from various sensors and switches, processing that information, and then outputting control signals to actuators and other devices.
The heart of a PLC is its programmable memory. This memory stores instructions that the PLC uses to make decisions and control the process. When you program a PLC, you're essentially telling it what to do when certain conditions are met. For example, you might program it to turn on a pump when the water level in a tank gets too low.
PLCs are built to be rugged and reliable. They can handle harsh industrial environments, with many designed to withstand vibration, moisture, and extreme temperatures. This makes them perfect for use in manufacturing, automation, and any situation where consistent and precise control is needed.
Now, let's talk about the different parts of a PLC. At its core, a PLC has three main components: the power supply, the central processing unit (CPU), and the input/output (I/O) modules. The power supply keeps the PLC running, the CPU does the thinking and decision-making, and the I/O modules are the gateway to the outside world, connecting the PLC to the devices it controls.
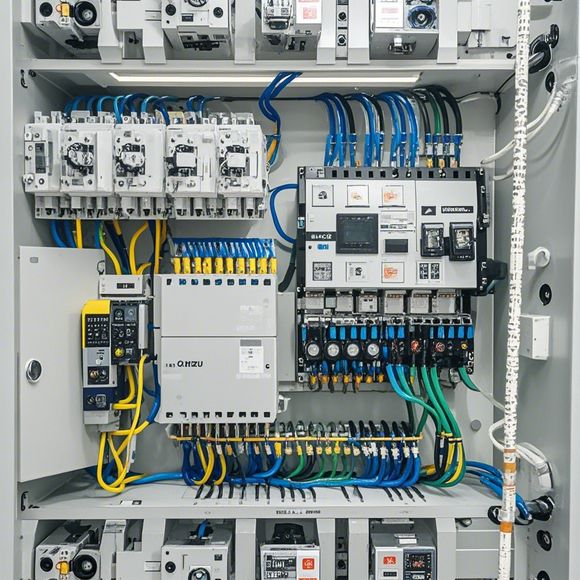
Inputs are how the PLC "sees" what's happening in the real world. This could be through switches, sensors, or even manual buttons. Outputs, on the other hand, are how the PLC "acts" on that information. They might control lights, motors, or any other device that needs to be turned on or off in a specific sequence.
Programming a PLC is usually done using a special programming language. Ladder Logic is one of the most common, as it's designed to be easy to understand for electricians and technicians who are familiar with electrical schematics. It's a visual language that uses diagrams that look like the rungs of a ladder, hence the name.
Once programmed, the PLC will run through its instructions in an endless loop, checking inputs, making decisions, and controlling outputs accordingly. This process is known as the scan cycle, and it happens so fast that the controlled system appears to operate in real-time.
PLCs are incredibly versatile and can be found in a wide range of applications. From controlling the conveyor belts in a factory to managing the temperature in a refrigeration system, PLCs are essential for ensuring that processes run smoothly and efficiently.
In summary, PLCs are powerful tools that use programmable memory to control various electromechanical processes. They're robust, reliable, and can be programmed using languages like Ladder Logic to perform complex tasks. Whether you're in manufacturing, automation, or any other field that requires precise control, understanding how PLCs work is key to keeping things running smoothly.
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Smart Manufacturing Solutions with PLC Integrated Machinery
The cost of a PLC Controller: A Comprehensive Analysis
PLC Programming for Automation Control in the Manufacturing Industry
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations
PLC Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Their Prices