PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) - The Powerful Tool for Automation
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is an incredibly powerful tool for automation. It can be programmed to perform a vast array of tasks, from simple logic functions to complex systems control. With the ability to program multiple inputs and outputs, PLCs can be used in many different applications, from small industrial machinery to large scale factories. They are especially helpful when it comes to safety and efficiency, as they allow machines to operate safely without human intervention. In addition, PLCs can be easily connected to the internet or other digital systems, allowing for real-time monitoring and control over large scale systems. Overall, PLCs are an essential part of modern manufacturing and industrial operations, providing efficient and reliable automation solutions.
In the world of manufacturing, automation is the backbone that drives industrial efficiency and productivity. And what better way to achieve this efficiency than with Programmable Logic Controllers, or PLCs? These are intelligent devices that can handle complex processes, making them indispensable for modern factories. In this guide, we're going to dive deep into the four core components of a PLC, each with its unique features and capabilities. So let's start by exploring the basic structure of an industrial PLC system, which consists of four key modules: input/output (I/O), processing logic, memory, and communication.
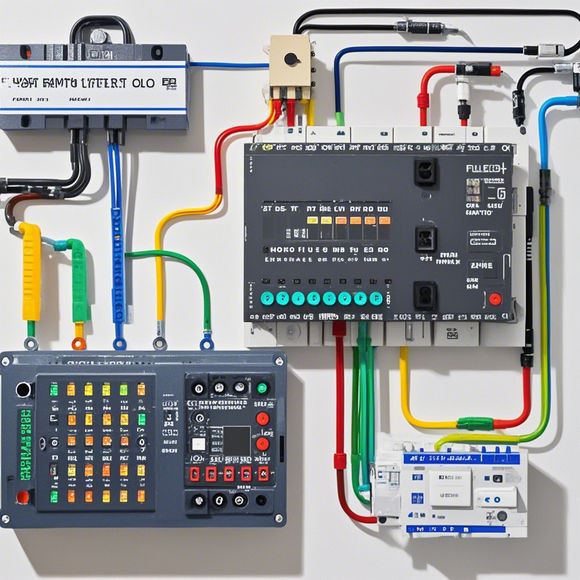
Input/Output Module
The I/O module is the gateway to the outside world for all your sensors and actuators. It's where data from various sources like machines, sensors, or even people enter the PLC system, and it's also where the results of calculations or decisions made by the processor go. This module is crucial as it allows you to collect real-time data and feed it directly into the control system.
Processing Logic Module
The processing logic module is the brain of the PLC. It's where you put all your algorithms, procedures, and instructions for controlling the system. This module uses stored programming code to process inputs and generate outputs based on predefined rules or conditions. Whether you're regulating temperature in a bakery or coordinating production lines at an automotive plant, the processing logic module ensures that your system runs smoothly and effectively.
Memory Module
The memory module is like a digital brain that stores all your program information, including instructions, data tables, and configuration parameters. It's important because without it, the PLC wouldn't have any functionality. You can store your programs in different formats, such as ladder diagrams or function blocks, and load them onto the PLC when needed.
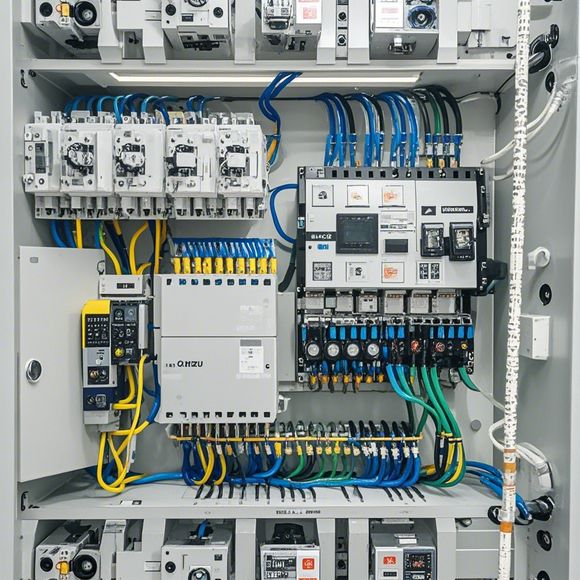
Communication Module
Lastly, but not least, the communication module is responsible for connecting your PLC to other systems in the factory network. It enables you to send commands, receive feedback, and exchange data between your PLC and other devices, such as computers or external hardware. With this module, you can create a seamless communication ecosystem that keeps your factory running smoothly.
So there you have it! The four essential modules of a Programmable Logic Controller, each playing a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation of your factory. If you want to stay ahead of the curve in automation, investing in a high-quality PLC system is essential. Remember, a good PLC is not just about speed and accuracy; it's also about reliability and flexibility. Choose wisely, and watch your factory thrive under the guidance of these intelligent controllers.
Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
PLC Controller Selection Guide for Foreign Trade Operations
Mastering the Art of Plc Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understand and Implement
The cost of a PLC Controller: A Comprehensive Analysis
PLC Programming for Automation Control in the Manufacturing Industry
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations