Introduction to the Four Major Modules of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
Sure, I can generate a summary of the four main modules in Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC).1. Process Control Module: This module is responsible for monitoring and controlling the industrial processes. It includes sensors and actuators that measure and adjust the process parameters to achieve desired results. The control algorithm determines the optimal operating conditions based on the measured data and sends commands to the actuators to make the necessary adjustments.2. Data Acquisition Module: This module is responsible for collecting and processing data from various sources such as sensors and other devices. It stores this data in a memory system for future analysis. The data acquisition module also performs signal conditioning and filtering to improve the accuracy and reliability of the measurements.3. Input/Output Interface Module: This module is responsible for connecting and communicating with external systems. It provides a communication interface for inputting commands to the PLC, receiving feedback from the process, and outputting data to other devices. The input/output interface module ensures that the PLC can communicate effectively with other systems and components in the industrial environment.4. Programming Interface Module: This module is responsible for programming and configuring the PLC. It allows users to write or modify the program code that controls the PLC. The programming interface module includes a user-friendly interface for writing and editing programs, as well as support for different programming languages.These are the four main modules of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) and they play a crucial role in controlling industrial processes efficiently and effectively.
Hello everyone, today we will delve into the fascinating realm of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). These marvels of technology are like the lifelines of modern industrial automation. They are the backbone of manufacturing and industrial control systems, enabling seamless integration of various production processes. In this discussion, we will explore the four main modules that form the heart of PLCs: the CPU (Central Processing Unit), I/O modules, memory modules, and communication modules. Each module plays a unique role in orchestrating the overall functionality and efficiency of the PLC system.
Firstly, let's talk about the CPU, often referred to as the brain of the PLC. It is the central processing unit that handles the complex logic operations required for decision-making, control, and monitoring. The CPU executes programs stored in flash memory or RAM, performing calculations and generating output signals based on predefined rules or data inputs. Its ability to process vast amounts of data and respond quickly to changing conditions sets it apart as the most critical component in the PLC system.

Moving on to the I/O modules, they serve as the gatekeepers between the CPU and external devices, allowing communication and input/output operations. These modules are designed to interface with sensors, actuators, motors, and other control elements in the industrial environment. They convert raw sensor data into useful information that can be processed by the CPU, while simultaneously relaying control commands to the actuators to perform tasks such as adjusting temperature levels or regulating pressure settings. The robustness and reliability of these I/O modules are essential for maintaining the smooth functioning of the industrial process.
Next up is the memory module, which stores program code and data used by the CPU for execution. It consists of two types: ROM (Read Only Memory) and RAM (Random Access Memory). ROM is non-volatile memory that holds firm programming instructions, making them permanent once written. This ensures that the PLC can operate reliably even when power is off. On the other hand, RAM is volatile, which means it loses its content when the power is turned off. However, it provides quick access to data and allows for real-time processing of incoming signals. The balance between these two types of memory determines how quickly the PLC can respond to changing conditions.
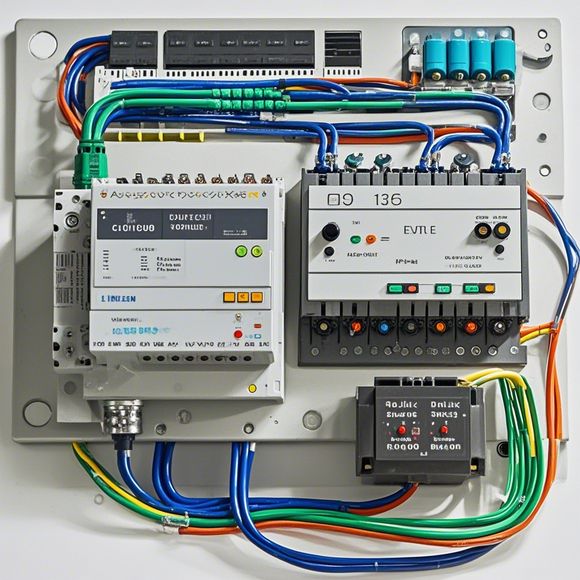
Finally, we have the communication module, which is responsible for transmitting data and commands from the CPU to external devices and vice versa. This module includes both analog and digital communication protocols, enabling PLCs to interface with a range of hardware and software systems. The choice of communication module depends on the specific application and network requirements, including factors such as bandwidth, latency, and security. By ensuring efficient and reliable communication between PLCs, industrial automation systems can operate more smoothly and effectively.
In conclusion, the four main modules of a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) play a pivotal role in shaping the performance, reliability, and flexibility of industrial automation systems. By understanding their functions and capabilities, we can optimize PLC usage and ensure that our industrial processes run smoothly and efficiently. Let's continue our journey through the wonders of PLC technology and discover the many applications that these intelligent controllers have to offer. Thank you for joining me on this enlightening discussion.

Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The cost of a PLC Controller: A Comprehensive Analysis
How to Use a PLC Controller for Your Business
Plumbers Rule! The Role of PLC Controllers in the World of Waterworks
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations
PLC Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Their Prices