PLC Modules in the Context of Modern Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide
In the modern manufacturing landscape, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) modules play a crucial role. These modules offer a flexible and efficient way to manage complex industrial operations. By leveraging their advanced features, manufacturers can optimize production lines, improve quality control, and enhance overall efficiency. This comprehensive guide provides a thorough overview of how PLC modules can be integrated into modern manufacturing processes. It covers everything from choosing the right modules for specific applications to troubleshooting common issues. Whether you're a seasoned expert or just starting your journey in this field, this guide will help you harness the power of PLC modules to drive innovation and success in your manufacturing business.
Hello everyone! Today, I'm here to talk about a crucial aspect of modern manufacturing - the role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). PLCs are digital controllers used in industrial automation systems, and they play a significant role in streamlining production processes, enhancing efficiency, and improving safety standards. In this guide, we will delve into the four main modules of PLCs and discuss their functionalities, installation, and maintenance. So, if you're looking to upgrade your factory's automation system or just want to know more about PLCs, keep reading!

Firstly, let's talk about the Central Processor Unit (CPU) module. The CPU is the brain of the PLC, responsible for processing instructions, data, and communicating with other modules. It has multiple functions:
1、Data Processing: The CPU performs calculations and logic operations on the received input data. It generates output signals based on the processed data.
2、Interfacing with Other Modules: The CPU communicates with other modules, such as sensors and actuators, through communication protocols like PROFIBUS, Modbus, or Ethernet.
3、Control Logic: The CPU executes control algorithms that determine the sequence and timing of actions. It also handles emergency stops and fault isolation.
4、Error Handling: If an error occurs during the execution of a program, the CPU can take corrective action, such as reverting to a safe state or triggering alarms.
Now, let's move on to the Power Module. This module supplies the necessary power to the PLC, ensuring it operates correctly even when there's a power failure. The power module consists of a transformer, capacitor, and relay, among other components. Its main function is to stabilize the supply voltage and provide a backup power source in case of power outages. The power module ensures that the PLC remains operational during emergencies or when the main power goes out.
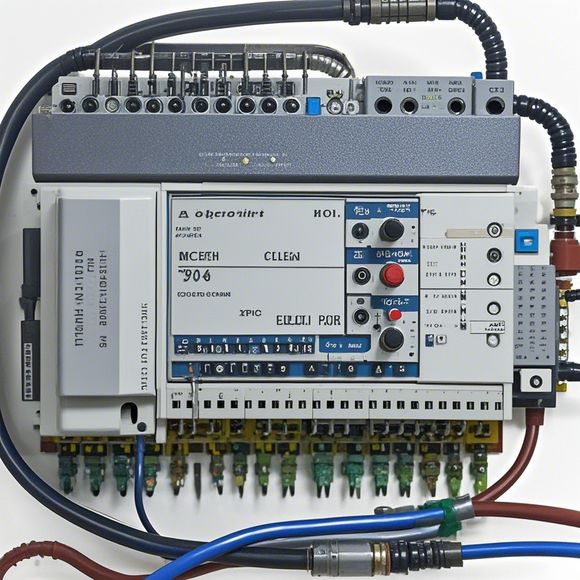
Next, we have the Input/Output (I/O) Module. The I/O module is responsible for receiving and transmitting data from external devices to the PLC and vice versa. It includes various types of switches, buttons, and sensors that allow the PLC to interface with different types of inputs and outputs. The I/O module enables the PLC to interact with other systems in the factory, allowing for automated control and monitoring.
Now, let's talk about the Communication Module. This module plays a crucial role in enabling the PLC to communicate with other devices in the plant network. It uses various communication protocols like PROFINET, PROFIBUS, Ethernet, or Modbus to send and receive data. The communication module ensures that information flows smoothly between PLCs, other devices, and the operator's console, making it easy to monitor and control the entire plant network.
Finally, let's talk about the Relay Module. This module is responsible for converting electrical signals into physical movement, such as opening or closing switches or actuators. The relay module is essential in many applications where direct physical interaction with the system is required. It allows the PLC to send signals that activate motors, valves, or other devices, without directly interfacing with them.
In conclusion, PLCs are critical components in modern manufacturing systems, providing a reliable and efficient means of controlling and monitoring production processes. By understanding the four main modules of PLCs - Central Processing Unit (CPU), Power Module, Input/Output (I/O) Module, and Communication Module, you can ensure that your factory runs smoothly and efficiently. Remember to regularly update and maintain your PLC system to ensure its optimal performance and longevity. Thanks for listening!
Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Mastering the Art of Plc Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understand and Implement
The cost of a PLC Controller: A Comprehensive Analysis
PLC Programming for Automation Control in the Manufacturing Industry
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Control System Basics
Plumbers Rule! The Role of PLC Controllers in the World of Waterworks
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations