Introduction to Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), also known as Programmable Logic Controllers, are electronic devices that allow for the automation of industrial processes. They are designed to control and monitor various systems by executing instructions stored in their memory based on inputs from sensors and actuators. The primary function of PLCs is to manage and regulate industrial processes efficiently, making it possible to automate complex tasks without requiring human intervention. These devices come with a wide range of capabilities, including fault detection, process monitoring, and data logging. In addition, they are often equipped with advanced programming languages that make it easy to program and customize the behavior of the device according to specific industrial needs. PLCs are widely used in various industries, such as manufacturing, power generation, and transportation, among others, due to their ability to improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and enhance safety.
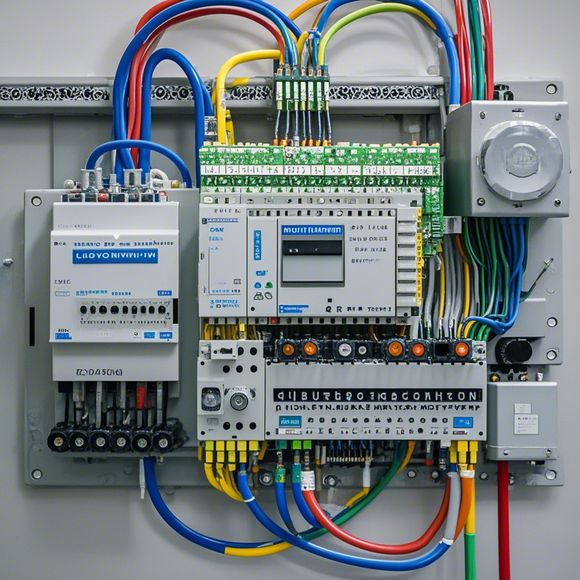
In the world of manufacturing, automation is a critical component that ensures efficient and reliable operation of industrial equipment. One of the most versatile and widely used tools for automation is the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC). PLCs are designed to handle complex control tasks by executing pre-programmed sequences of instructions. In this guide, we will delve into the intricacies of how PLCs work, covering their basic components, how they communicate with other devices, and some common applications in various industries. By understanding the fundamentals of PLCs, you can effectively integrate them into your business operations to achieve greater efficiency and cost savings.
Firstly, let's start with the core components of PLCs:
- Input/Output (I/O) modules: These modules serve as the interface between the PLC and the external hardware devices. They receive signals from sensors and actuators and send commands to control the corresponding devices. The I/O modules can be classified based on their function: analog, digital, or mixed signal.
- Central processing unit (CPU): The CPU is the brain of the PLC, responsible for interpreting the input data, performing calculations, and generating output commands. The CPU is usually located in a separate cabinet or module.

- RAM and ROM: These components store the PLC program code and user data, respectively. The RAM stores the running program while it is active, while the ROM stores the entire PLC program once the device is powered off.
- Power supply: The power supply provides energy to the PLC, ensuring it operates without interruptions.
- Communication interfaces: PLCs can communicate with other devices through different protocols such as Profinet, Profibus, or Modbus, allowing for seamless integration with existing automation systems.
Now, let's explore some key features of PLCs:
- Simplicity: PLCs are designed to be user-friendly and easy to install. They come with comprehensive documentation and support, simplifying the process of setting up and configuring the device. Additionally, PLCs often include built-in diagnostic tools that allow for quick troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Reliability: PLCs are known for their high reliability due to their robust design and redundant components. They are designed to withstand extreme conditions and operate continuously without requiring frequent replacements. This ensures that they remain reliable even in harsh industrial environments.
- Versatility: PLCs can be customized to meet specific requirements and can handle a wide range of control tasks. They can be used in various industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics, among others. The flexibility of PLC programming allows for customization based on the specific needs of the application.

- Cost-effectiveness: Compared to other types of automation, PLCs offer significant cost savings due to their simplicity and reliability. They require fewer components and can be easily integrated into existing systems, reducing the need for extensive modifications or additional hardware. Additionally, PLCs can be purchased individually or as part of a larger automation system, making it easier to budget for and manage the costs associated with automation projects.
Moving on to how PLCs communicate with other devices, there are several ways they can interact:
- Serial communication: PLCs can communicate with other devices using serial ports, which provide a simple way to transfer data over long distances. Serial communication is commonly used in systems where speed is not an issue and where the communication protocol is well understood.
- Ethernet networking: With the emergence of Ethernet networks, PLCs can now communicate with each other and other devices over a local area network (LAN). This allows for faster data transfer rates, increased security, and better integration with cloud-based solutions.
- Modbus communication: Modbus is a popular protocol for PLC communication that offers a standardized way to exchange data between devices. It is widely used in industrial automation because it is flexible, reliable, and easy to implement.
- Industry standards: There are several industry standards that define the communication protocols between PLCs and other devices, such as PROFINET, PROFIBUS, and HART. These standards ensure that different manufacturers can interoperate with each other and that data exchange is consistent and reliable.
Now, let's dive into some common applications of PLCs in various industries:
- Manufacturing: PLCs are essential tools for managing complex production lines and ensuring efficient assembly of products. They can automate tasks such as material handling, machine monitoring, and quality control, leading to improved productivity and reduced downtime.
- Healthcare: In healthcare settings, PLCs are used in patient monitoring systems, medical equipment control, and laboratory automation. For example, they can monitor vital signs and adjust equipment settings based on patient data, improving patient care and safety.
- Logistics: PLCs play a crucial role in managing warehouse operations, inventory management, and transportation planning. They can optimize storage space, reduce handling errors, and improve overall efficiency.
- Energy: In the energy sector, PLCs are used for controlling renewable energy sources such as wind and solar farms. They can regulate power generation, monitor equipment performance, and ensure safe operations in hazardous environments.
In conclusion, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are powerful tools that offer significant benefits for businesses looking to streamline their operations and increase efficiency. By exploring the basic components and communicating methods of PLCs, along with their applications in various industries, you can gain a deeper understanding of how these devices can transform your business. Remember, investing in PLCs is a smart move that will pay off in terms of reduced costs, improved productivity, and enhanced safety. As your business grows, so too will your reliance on PLCs to stay ahead of the competition and achieve sustainable success.
Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Smart Manufacturing Solutions with PLC Integrated Machinery
How to Use a PLC Controller for Your Business
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Control System Basics
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations
Connecting a PLC Controller to Your Computer
PLC Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Their Prices