PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Modules
Sure, based on your description of PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) modules, here's a concise summary in English:"The Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) module is a key component in industrial automation systems. These modules are designed to be programmable and control various types of industrial processes, such as manufacturing lines, assembly lines, and chemical plants. The PLC module is equipped with a microprocessor that can execute complex algorithms and instructions for the specific task at hand. This makes it highly adaptable and versatile, allowing for easy customization and modification according to different production requirements."
In the realm of industrial automation, PLCs play a pivotal role as they enable precise control and monitoring of complex processes. These versatile devices consist of four core modules, each with its unique set of functionalities that contribute to the overall functionality of an PLC system.
The first module is the Central Processor Unit (CPU), which serves as the brain of the PLC. It handles all the calculations, logic operations, and data processing required for the execution of programs. The CPU is responsible for interpreting input signals and generating output signals to control the actuators. Its performance determines the responsiveness of the PLC system, making it crucial to ensure that it is reliable and efficient in handling high-speed data streams.
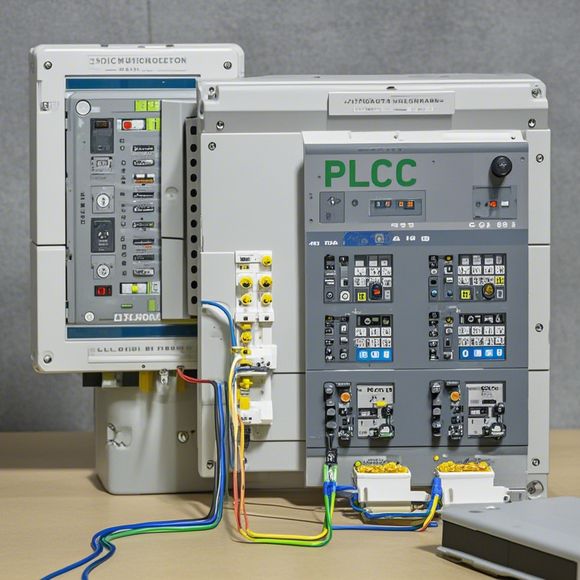

Next comes the Programmable Logic Element (PROFET), which is responsible for implementing user-defined logic functions. PROFETs can be programmed using different programming languages like Ladder Diagrams, Function Block Diagrams (FBD), or Structured Text (ST). Their flexibility allows users to tailor the behavior of the PLC to specific applications, making them a powerful tool for creating customized solutions.
The next module is the RAM (Random Access Memory), which stores the program code executed by the CPU during runtime. This memory is used to store the instructions that are executed when the PLC is turned on, allowing for rapid startup and reduced power consumption. The size of the RAM determines the maximum number of programs that can be stored, with larger RAMs supporting more complex applications.
Finally, we have the Input/Output Devices (I/O) modules, which are responsible for receiving and transmitting information between the PLC and other components in the system. I/O modules come in various forms, including relays, switches, and sensors, enabling the PLC to interface with mechanical systems, electrical circuits, and environmental variables. Their reliability and speed are critical factors in maintaining the overall performance of the PLC system.
In summary, PLCs consist of four core modules: CPU, PROFET, RAM, and I/O devices. Each module plays a vital role in ensuring that the PLC system is capable of performing complex tasks efficiently and reliably. By understanding the function of each module and their interrelationship, businesses can optimize their PLC systems, improve productivity, and reduce costs.
Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The cost of a PLC Controller: A Comprehensive Analysis
How to Use a PLC Controller for Your Business
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Control System Basics
Plumbers Rule! The Role of PLC Controllers in the World of Waterworks
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations
PLC Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Their Prices